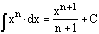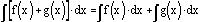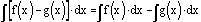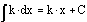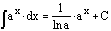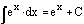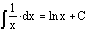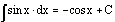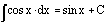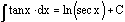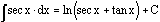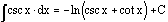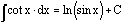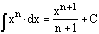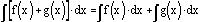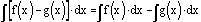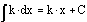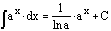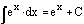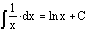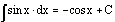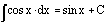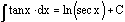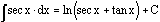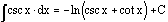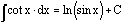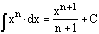 |
The
integral of a power is the reciprocal of the exponent plus one times x to
the power of the exponnent plus one.
|
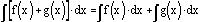 |
The
integral of a sum is the sum of the integrals of each function being added.
|
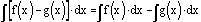 |
The
integral of a difference is the difference of the integrals of the functions
being subtracted.
|
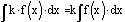 |
The
integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral
of the function.
|
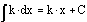 |
The
integral of a constant is the constant times x.
|
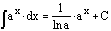 |
The
integral of an exponential function is the product of the exponential function
and the reciprocal of the natural logarithm of the base.
|
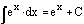 |
Since
the natural logarithm of e is 1, the integral of e^(x) is e^(x).
|
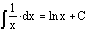 |
The
integral of 1 divided by x is the natural logarithm of x.
|
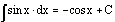 |
The
integral of the sine of x is the opposite of the cosine of x.
|
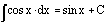 |
The
integral of the cosine of x is the sine of x.
|
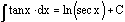 |
The
integral of the tangent of x is the natural logarithm of the secant of x.
|
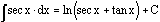 |
The
integral of the secant of x is the natural logarithm of the sum of the secant
of x and the tangent of x.
|
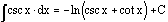 |
The
integral of the cosecant of x is the opposite of the natural logarithm of
the sum of the cosecant of x and the cotangent of x.
|
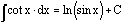 |
The
integral of the cotangent of x is the natural logarithm of the sine of x.
|